Art, the Hungryalists, and the Beats
By Juliet Reynolds
As both movements were predominated by
poets and writers, there can be few to argue with the established
perception that the Beat Generation and the Hungry Generation were
primarily literary in character. While the two movements have tended to
invite comparison with the Dadaists, no-one would define either as an
‘art movement’, as Dada so patently was, its literary associations
notwithstanding.
Yet a closer look at the history and
legacy of the Beats and the Hungryalists reveals beyond doubt that
visual art and artists occupied a more pivotal place in their movements
than is generally supposed. This seems at first reckoning to be truer of
the Beat movement, whose annals contain a riveting art narrative that
runs from their very beginnings and has barely come to a stop. Of
course, it must be borne in mind that Beatdom is much better documented
and appraised than Hungryalism, thanks in the main to the First
World-Third World divide. While the Beats’ counter-culture evolved in
the most powerful nation on earth, the Hungryalists’ took shape in an
impoverished, underdeveloped country, that too in a single state or
region.
Moreover, Hungryalism was politically
suppressed in a way and to an extent that Beatdom was not. Ginsberg,
Kerouac, Ferlinghetti, Corso, Burroughs and the rest could turn their
notoriety to advantage, even if they didn’t desire it. This would allow
their movement to endure and evolve so that it would live on in the
collective consciousness and become a cult.
On the other hand, the movement launched
in 1961 by Malay Roychoudhury, Shakti Chattopadhyay, Samir Roychoudhury
and Debi Roy was decimated within a few years due to official hounding
as well as internal strife, a good deal of it fomented precisely because
of the harassment. The prosecution of Malay and others for obscenity
and his subsequent imprisonment was but part of the Bengal
administration’s crackdown on Hungryalism. Booked for conspiracy, every
member of the group was subjected to ruthless police raids resulting in
the confiscation of their intellectual and personal property, including
books, writings and letters. The Hungryalist artists – Anil Karanjai,
Karunanidhan (Karuna) Mukhopadhyay, and others attached to their studio
in Banaras, named the Devil’s Workshop – witnessed the seizure of their
art works and all

Anil Karanjai, The Dreamer, 1969
records of the movement, never to see
their restitution. Fortunately, a body of Anil’s work, created in the
immediate post-Hungryalist era, remained in his hands or became part of
collections, and because the imagery this encompasses is strongly marked
by the ideas and concerns of the movement, it provides the basis for a
more comprehensive understanding of Hungryalism. It’s not a cliché to
state that images so often speak more eloquently than words.
Just as Anil Karanjai (1940-2001) was the only adherent of the Hungry Generation to dedicate his life to art,

Portrait of Allen Ginsberg by Robert LaVigne, c. mid-1950s
there was a sole true Beat painter,
Robert LaVigne (1928-2014). As recorded by Allen Ginsberg, LaVigne had
helped give birth to the Beat Generation. The artist’s roomy house in
San Francisco was a gathering place for the wild, unclothed ‘bohemians’
of all genders who personified the movement. LaVigne did graphics and
poster art for the group, as well as producing his own paintings. Anil
and Karuna worked similarly with the Hungryalists.
Ginsberg and LaVigne shared aesthetic
concerns. They both focused on themes of decay and death reflecting the
angst of the young generation in the Atomic Age which, to quote LaVigne,
‘gave the lie to permanence’. The question of
creating durable art in a world with no future had a paralysing effect
on him, a state he might not have come out of had he not discovered
Beatdom. ‘The mad, naked poet’, as Ginsberg was known, and ‘the naked,
great painter’, as Ginsberg

Sketch of a Young Girl, Anil Karanjai 1991
described LaVigne, both created telling
portraits of friends and intimates, the former searingly in ‘Howl’, the
latter more gently in lines and colour. His oil portrait of the young
Ginsberg illustrates this amply.
In contrast to his Beat counterpart, Anil
Karanjai came to portraiture quite late in his life. Stylistically, the
two artists are at variance but in several of their portraits there is a
similar expression of tenderness for the subject. This is much in
evidence, for instance, in Anil’s charcoal sketch of Karuna’s young
daughter, a girl Anil had known since birth and who had been almost a
mascot for the Hungryalist artists.

Portrait of Peter Orlovsky by Robert LaVigne, c. mid-1950s
Ginsberg’s favourite work by his painter
friend LaVigne, also his rival in love, was a huge portrait of the young
Peter Orlovsky. Naked with an uncircumcised penis and crop of dark
pubic hair, the work is sexually charged but it is also sad and
contemplative. Ginsberg wrote that when he first saw the portrait,
before ever meeting the subject, he ‘looked in its eyes and was shocked
by love’. By the standards of the day, Ginsberg and LaVigne were both
pornographers. But unlike the poet, the painter managed to evade
prosecution, a remarkable feat given that full-frontal nudity was deemed
obscene until the early 1970s and homosexuality was a cognizable
offence.
Like Robert LaVigne, Anil Karanjai
painted nudes, without legal repercussions. But, as may be remarked in
his romantic canvas ‘Clouds in the Moonlight’ (1970), the Hungryalist
was more of a visionary than the Beat painter.

Anil Karanjai, Clouds in the Moonlight, 1970
The grand poet and co-founder of City
Lights, Lawrence Ferlinghetti, who was charged with obscenity for
publishing ‘Howl’ and who published the Hungryalists when they were
standing trial, was also a painter of considerable accomplishment.
Ferlinghetti’s expressionistic imagery – the earliest semi-abstract, the
later figurative and often directly political – is very compelling and
underlines his deep commitment as an activist.
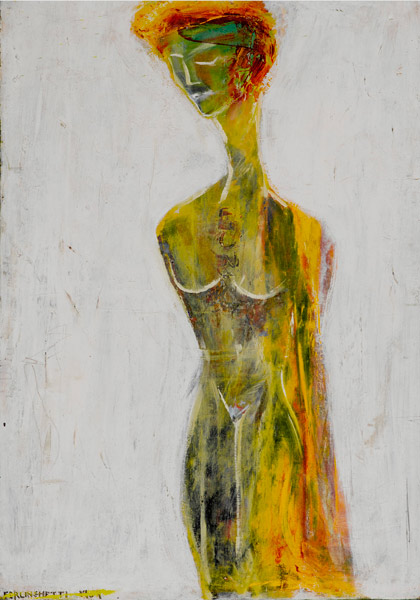
Lawrence Ferlinghetti, Against the Chalk Cliffs, 1952-7
The prosecuted author of ‘Naked Lunch’,
William Burroughs, is a further major figure of the Beat Generation to
have been a visual artist. But the paintings and sculptures of Burroughs
are literal horrors. He was known at times to have painted with his
eyes shut in order to explore his psyche, which was considerably
deranged, not just by an overload of hard drugs and perverse sexual
drives. Some of his canvases are riddled with bullet holes, a reminder
to his viewers that he shot his wife to death while playing William
Tell, mistaking her head for a highball. Later known as ‘the father of
Punk’, Burroughs enjoyed a friendship with the ‘father of Pop Art’, Andy
Warhol, himself no stranger to guns, even if as victim rather than
shooter. Burroughs was a frequent visitor to Warhol’s New York studio,
known as ‘The Factory’.
In their earlier days, the Beats were
loosely linked to the Abstract Expressionist painters and although the
latter were not quite so flagrant in their unorthodox personal lives,
they shocked the media and public in equal measure when it came to their
work. They also created in a similar vein, eschewing conventional art
forms and expressing themselves spontaneously; to achieve this end, they
applied rapid, fluid strokes on outsized

Anil Karanjai, Summer Morning (detail) 1971
canvases; this was consistent with ‘the
orgasmic flow’ that was a lynchpin of Hungryalism. Abstract
expressionist paintings may appear anarchic but, in common with the
writings of both the Beats and the Hungryalists, their art was
conceptual in construct; in essence, their chaos was planned.
The image of the artist creating in a
frenzy of uncontrolled passion is but a cliché, and few painters
underlined this more cogently than Anil Karanjai. Even as a neophyte,
full of fury and restless energy, he produced painstaking, considered
work. If anything, his experience with the Hungryalists, among whom he
was one of the

Hieronymus Bosch The Garden of Earthly Delights (detail) late 15th-early 16th century
youngest, served to heighten these
qualities. The only western painter to have influenced him in any way
was the Dutch master, Hieronymus Bosch (c. 1450–1516). Bosch’s grotesque
satirical imagery inspired Anil as he struggled to create his own
unique vision of the hierarchical, oppressive society around him.
Abstract Expressionism was unknown to Anil until much later on.
The most notorious Abstract
Expressionist, Jackson Pollock – ‘Jack the Dripper’ – likewise an
‘action painter’, is one of several artists who finds a place among the
writers at The American Museum of Beat Art (AMBA) in California. So too
is the supreme Dadaist, Marcel Duchamp, who had coined the term
‘anti-art’ before any of the Beats were born and was, therefore, one of
their idols. But the story goes that when Allen Ginsberg and Gregory
Corso met Duchamp in Paris in the late 1950s, they were so inebriated
that the former kissed his knees while the latter cut off his tie; by
now an elder of the art world, Duchamp was probably not amused. The
Beats’ conduct in those days could be so selfishly outrageous that they
managed to antagonise many, including Jean Genet, hardly known for model
behaviour himself.
It’s doubtful whether the subject of art
arose in a meaningful way between Anil Karanjai and Allen Ginsberg when
they spent time together in Banaras. The American had his mind on
‘higher things’, namely sadhus, burning ghats, mantras and ganja. Apart
from introducing Ginsberg to the harmonium, in the company of the
Buddhist, Hindi poet, Nagarjuna, Anil and Karuna taught Ginsberg and
Orlovsky the art of chillum-smoking, an almost ritualistic activity, not
at all easy to master. Otherwise, Ginsberg appears to have shown little
curiosity about the art of the Hungryalists. This did not offend Anil
who was then very young, thrilled to have the opportunity to converse in
English, a language with which he was not then familiar. Neither Anil
nor Karuna would have been overawed by the feted American, but Anil
would sometimes quote him later: “America when will you send your eggs
to India?”, from the poem America, was a favourite line.
Ginsberg no doubt was not a racist, not
at least on a conscious level. But there was an element of white man’s
arrogance within him, as there surely was in other Beats. Despite being
an anti-establishment movement, it was at some levels a highly elitist
one as well. Burroughs, for example, seems to have got away with his
wife’s killing because he was a Harvard alumnus and came from a rich
family. The background of Ginsberg was not quite so privileged but he
rose to superstardom young. No amount of ‘slumming-it’ in India could
change that, could knock him from his pedestal; in addition, he must
have been treated to a fair share of ‘chamchagiri’ during his travels.
Probably the Hungryalists were among the few to exchange ideas with him
as equals, and his failure to acknowledge their impact on his poetry and
thinking reflects poorly upon him.
Ginsberg, who was evidently quite taken
by religion in India, may not have entirely appreciated the
Hungryalists’ views on the subject. They denounced god and all forms of
belief and worship in the most condemnatory of terms. Anil’s upbringing
in Banaras had rendered him particularly irreligious; he’d been
challenging temple elders since the age of 12, often defeating them with
his superior knowledge of the Hindu scriptures and his sharp tongue.
With a scientific bent of mind, he would remain a staunch atheist
throughout his life. Early Buddhism did appeal to him, but he was
critical of the Tibetan form of Buddhism, later embraced by Allen
Ginsberg. Of course, the Beat poet’s anti-war politics and activism did
accord with Anil’s worldview, as it must have with others of the
erstwhile Hungry Generation.
As far as the Hungryalists’ politics was
concerned, Anil was at one with their ferocious attack on the entrenched
establishment, but he rejected their anarchism, their precept that
existence is ‘pre-political’ and that all political ideologies should be
precluded. He had enrolled in and quit the Communist Party much prior
to joining Hungry Generation, but he would thereafter remain committed
to the far left. It is a myth he became a Naxalite when Hungryalism
fizzled out.
There is truth in the legend that the
Hungryalists engaged in sexual anarchy in Banaras and Kathmandu, but
compared to the shenanigans of the Beats this was really quite tame.
Anil and Karuna did live with seekers and hippies in an international
commune, and indeed Karuna was its manager and sometimes head cook.
Further, a large part of their subversive activities did involve the
consumption of consciousness expanding substances including LSD, magic
mushrooms and the like, but their experiments were always undertaken in a
controlled environment. This did make a great mark on Anil but because
he never consumed substances irresponsibly, the outcome was positive,
helping to liberate and enhance his vision as a painter. This hardly
constituted ‘drug abuse’ as claimed by some.
Further, the deliberate burning of
paintings by their Hungryalist creators is a much exaggerated story,
largely based on the aftermath of an exhibition in 1967 at a well-known
Kathmandu gallery. The event coincided with a writers’ conference that
was attended by Malay and others who had remained loyal to Hungryalism.
It was Karuna alone who destroyed his work. Anil enjoyed the spectacle
but remained on the side-lines. Such anti-art gestures didn’t fit his
philosophy. His iconoclasm was of another kind.

Anil Karanjai, The Competition, 1968
Yet, whatever his divergences with
Hungryalist ideology, Anil shared the movement’s aesthetic concerns.
This is most immediately perceptible in his works of the late ’60s such
as ‘The Competition’. Painted in 52 straight hours in the Banaras
commune, the work is based on a banyan tree, a metaphor for the chaos
and struggle of the times. It also reflects the aspiration of the
Hungryalists, as well as that of the Beats, to reintegrate humans with
the natural world, a world in which obscenity is non-existent and lost
innocence is restored.
Although Anil’s work metamorphosed and
matured in his post-Hungry Generation decades, his experience with the
movement remained in his consciousness. His ideas may have come from
many sources, but he never lost sight of that Hungryalist goal. Much of
his late work is apparently classical, an expression of realism. His
landscapes in particular seem to be the antithesis of his early
‘surreal’ imagery and this tends to confound his viewers. But while it
is certainly true that the provocative, rhetorical imagery has vanished,
the foundations remain the same. From beginning to end, Anil’s art
expresses the drama of the human condition through the moods and forms
of nature. And this does accord with Hungryalist poetry. Take, for
instance, the lines of Shakti Chattopadhyay:
“Like a football the moon is poised over the hill
Waiting for the late night game and the war cries
At these moments you can visit the forest…”
Waiting for the late night game and the war cries
At these moments you can visit the forest…”
(Translated by Arunava Sinha)

Anil Karanjai, Moonrise, 1990
The poet conjures up an image very close
in mood and feeling to a late work of Anil’s, part of a series of
mysterious night landscapes. Binoy Majumdar also approaches the spirit
of this image when he says:
“all trees and flowering plants stand on their own
grounds at a distance forever
dreaming of breathtaking union.”
grounds at a distance forever
dreaming of breathtaking union.”
(Translated by Aryanil Mukherjee )
The concept of nature’s creations ‘dreaming of breathtaking union’ is echoed time and again in the life’s work of Anil Karanjai.
So too is the theme of the lonely creator
or thinker which he expressed with great range. In a canvas of 1969,
titled ‘The Dreamer’, the thinker is

Anil Karanjai, The Builder (watercolour), 1979
shaped by confrontational Hungryalism and
LSD, while a work in watercolour presents the theme in a way that
parallels a declaration of Malay Roychoudhury: “…for me, the first poet
was that Zinjanthropus who lifted a stone millions of years ago and made
it into a weapon.” Later, Anil’s solitary poets or philosophers, set in
stone, are encircled by nature, their only weapons their knowledge and
experience. All these works are executed with mastery. It reflects well
on Hungryalism that it is associated with an artist of such calibre and
originality.
…
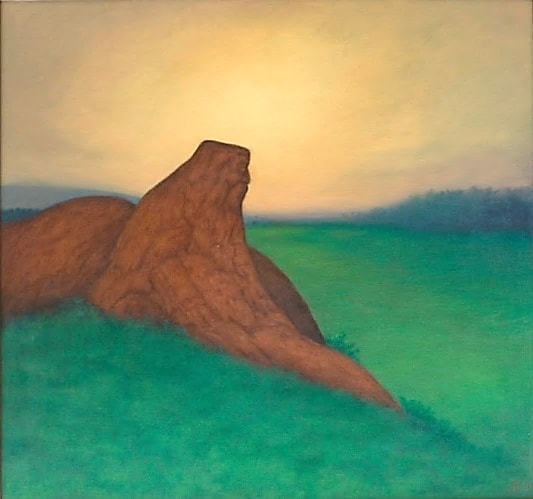

Anil Karanjai, Solace in Solitude, 2000
…
*All the works by Anil Karanjai
accompanying this piece belong to the collection of the writer, with the
exception of ‘The Dreamer’, which is in the collection of Anjana Batra,
New Delhi; ‘Clouds in the Moonlight’ is part of the collection of The
Kumar Gallery, New Delhi and New York.
…
Bio:
Juliet Reynolds is a critic and writer, specialising in Indian art and socio-cultural issues. Of mixed Irish-English descent, she was born in Ireland and educated in England, France and Italy. A gold medallist from the London Academy of Music and Dramatic Art, she worked for many years as an English and drama teacher with students of diverse ethnicity. Based in New Delhi and Dehradun, she has spent most of her working life in India. Here she has established a reputation as a resolute critic and commentator, and as a bridge between scholars and the lay reader. The publications to which she has contributed include The Spectator, The Insight Guide to India, The India International Centre Quarterly Review, The Pioneer and Biblio. She is the author of In the Eyes of a Rasika: a connoisseur’s view of art and politics, art and science (Srishti/Bluejay, 2003) and Finding Neema, (Hachette, 2013). Her late husband was the Hungryalist artist, Anil Karanjai.
Juliet Reynolds is a critic and writer, specialising in Indian art and socio-cultural issues. Of mixed Irish-English descent, she was born in Ireland and educated in England, France and Italy. A gold medallist from the London Academy of Music and Dramatic Art, she worked for many years as an English and drama teacher with students of diverse ethnicity. Based in New Delhi and Dehradun, she has spent most of her working life in India. Here she has established a reputation as a resolute critic and commentator, and as a bridge between scholars and the lay reader. The publications to which she has contributed include The Spectator, The Insight Guide to India, The India International Centre Quarterly Review, The Pioneer and Biblio. She is the author of In the Eyes of a Rasika: a connoisseur’s view of art and politics, art and science (Srishti/Bluejay, 2003) and Finding Neema, (Hachette, 2013). Her late husband was the Hungryalist artist, Anil Karanjai.
***
কোন মন্তব্য নেই:
একটি মন্তব্য পোস্ট করুন